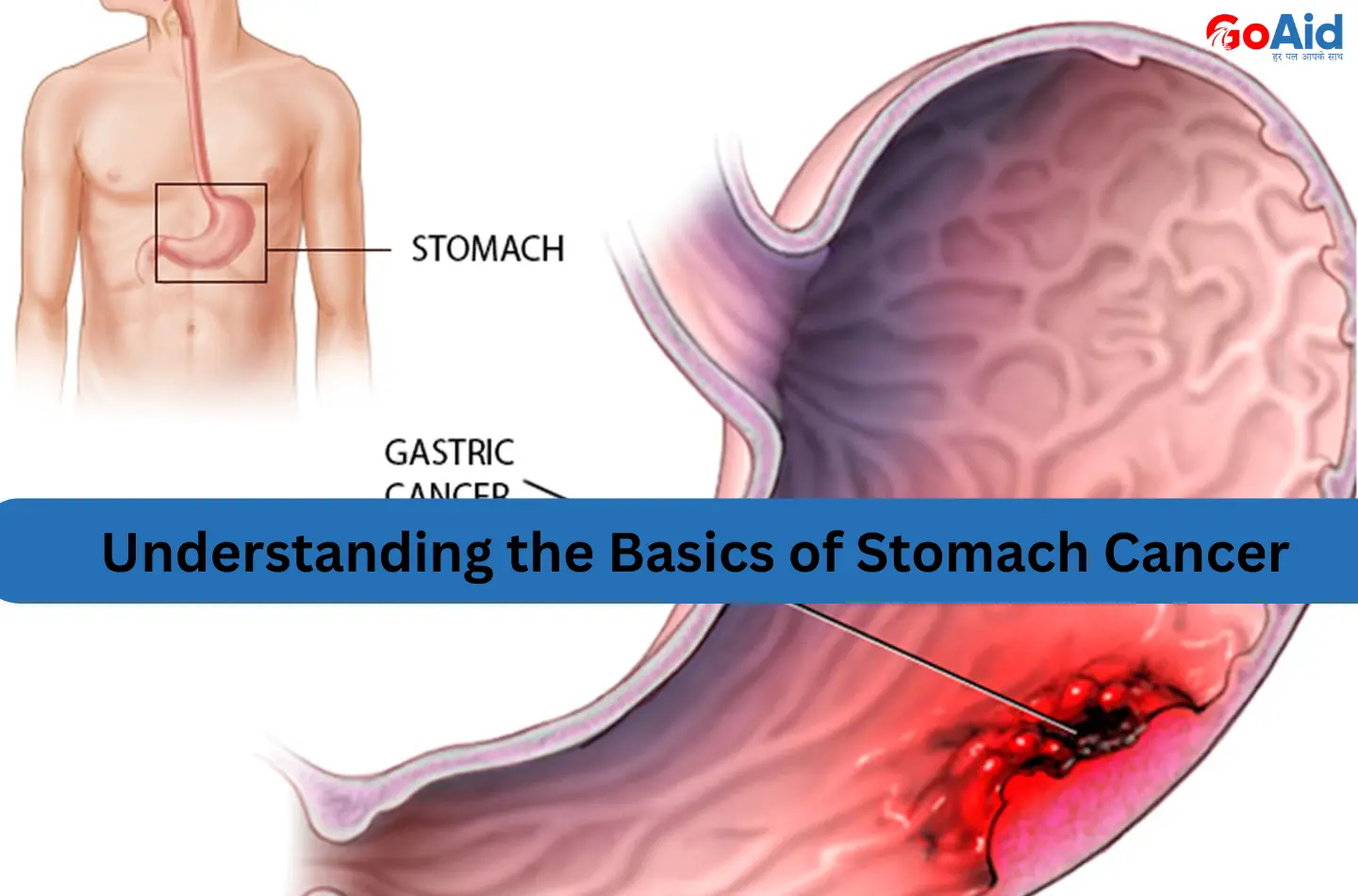
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is one of the most serious forms of cancer that begins in the lining of the stomach. In many cases, the disease develops slowly over years, often showing no major symptoms in its early stages.
ThatŌĆÖs why awareness about its causes, symptoms, and emergency care options is so important. GoAid, with its specialized ambulance services for cancer patients, ensures safe and reliable transportation during critical medical situations.
This is why, in this blog, we have provided you all the details about what stomach cancer is, its symptoms, causes, early diagnosis, GoAidŌĆÖs ambulance assistance for cancer patients, and essential care tips. Are you willing to know about all these points in detail? Then read this blog to the end.
So, letŌĆÖs start ŌĆō
What is Stomach Cancer (Gastric Cancer)?
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a condition in which malignant cells form in the lining or tissues of the stomach. It typically develops slowly over several years and often starts as small, precancerous changes in the stomach lining.┬Ā
If left untreated, these abnormal cells multiply uncontrollably, forming tumors that can invade deeper layers of the stomach and spread to other organs such as the liver, lymph nodes, or lungs. Early-stage stomach cancer may not show noticeable symptoms.
This makes it difficult to detect without regular medical checkups. Timely awareness, monitoring, and seeking help through GoAid Cancer Ambulance Service can ensure rapid medical attention. This improves survival chances and enabling access to specialized oncology treatment.
What Are the Main Causes and Risk Factors of Gastric Cancer?
Stomach cancer develops due to a combination of environmental, lifestyle, and genetic factors. Understanding the causes and risk factors is essential for prevention and early detection.
Causes:
- Helicobacter pylori Infection:
Chronic infection with H. pylori bacteria can inflame the stomach lining. This leads to precancerous lesions and eventual gastric cancer.
- Chronic Gastritis:
Long-term inflammation of the stomach lining increases cellular damage, potentially causing malignant changes in gastric tissues.
- Smoking:
Tobacco use contributes to DNA mutations in stomach cells, elevating the risk of cancer formation.
- Poor Diet:
Diets high in salty, smoked, or processed foods can irritate the stomach lining and increase cancer risk.
- Obesity:
Excess body weight raises acid reflux and inflammation, which may contribute to abnormal cell growth in the stomach.
- Previous Stomach Surgery:
Patients with prior stomach surgery may have altered digestive systems. This increases susceptibility to cancer over time.
- Family History of Gastric Cancer:
Genetic predisposition can increase susceptibility to stomach malignancies if close relatives are affected.
- Pernicious Anemia:
Reduced stomach acid production associated with anemia may lead to changes in the stomach lining and increased cancer risk.
- Long-Term Use of Certain Medications:
Prolonged use of medications like proton pump inhibitors may alter stomach acidity and influence cancer development.
- Exposure to Carcinogens:
Occupational exposure to harmful chemicals or carcinogens may increase the likelihood of stomach cancer.
Also Read: Early Signs of Diabetic Eye Disease
Risk Factors:
- Age Over 50:
Older adults are at higher risk due to cumulative cellular damage and slower tissue repair mechanisms.
- Male Gender:
Men are statistically more likely to develop gastric cancer than women, possibly due to hormonal and lifestyle differences.
- High Salt Intake:
Excessive consumption of salty foods can damage the stomach lining and increase cancer risk.
- Family History of Cancer:
Genetic factors and shared lifestyle habits contribute to elevated risk among relatives.
- Obesity and Metabolic Disorders:
Obesity and related metabolic issues can exacerbate gastric inflammation and cell mutation.
- Chronic Gastric Conditions:
Conditions like ulcers or chronic gastritis increase vulnerability to malignant changes.
- Tobacco Use:
Smoking not only causes mutations but also weakens the immune response against abnormal cells.
- Alcohol Consumption:
Heavy alcohol intake can irritate the stomach lining and increase susceptibility to cancer.
- Low Fruit and Vegetable Intake:
A diet lacking protective antioxidants can fail to counteract oxidative stress in gastric cells.
- Previous Radiation Therapy:
Radiation exposure to the abdominal area may increase long-term risk of gastric malignancies.
Also Read: How Pollution Affects Lungs Negatively
Common Symptoms of Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer often develops silently, but certain symptoms can indicate early-stage disease. This requires timely medical attention.
- Persistent Indigestion:
Ongoing discomfort or burning in the stomach may indicate changes in the stomach lining caused by abnormal cell growth.
- Nausea and Vomiting:
Frequent nausea, vomiting, or vomiting blood can signal irritation or obstruction from tumors in the stomach.
- Unexplained Weight Loss:
Significant and sudden weight loss may indicate that the body is unable to absorb nutrients due to stomach abnormalities.
- Loss of Appetite:
Early satiety or lack of appetite often occurs when tumors affect stomach capacity or signaling to the brain.
- Abdominal Pain or Discomfort:
Persistent pain, cramping, or bloating in the upper abdomen may indicate tumor growth or inflammation.
- Blood in Stool:
Dark or tarry stools can result from bleeding in the stomach lining caused by cancerous growths.
- Fatigue or Weakness:
Chronic blood loss or malnutrition caused by stomach cancer can lead to weakness, tiredness, and general malaise.
How Can Early Diagnosis of Stomach Cancer Be Done?
Early diagnosis of stomach cancer significantly improves treatment outcomes and survival rates. Medical professionals recommend regular screenings for high-risk individuals, especially those over 50 or with a family history of gastric cancer.
Diagnostic methods include endoscopy, where a small camera examines the stomach lining for abnormal growths or lesions. Biopsies taken during endoscopy confirm the presence of cancerous cells. Imaging tests like CT scans or PET scans help identify tumor size, location, and spread.
Blood tests can detect anemia or tumor markers associated with gastric malignancies. Patients experiencing persistent symptoms like abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, or vomiting blood should seek immediate medical attention.
GoAid Cancer Ambulance Service provides safe, fast transportation for suspected cancer patients. This ensures timely access to specialized oncology centers and expert medical care, which is critical for early intervention and better prognosis.
How Does GoAid Ambulance Offer Help for Cancer Patients Across India?
GoAid Ambulance ensures timely, safe, and specialized transportation for cancer patients. This provides medical support and rapid access to hospitals anywhere in India.
- Rapid Emergency Response:
GoAid Ambulance reaches patients quickly. This minimizes delays in critical situations. This ensures cancer patients receive immediate attention and stabilization during transport.
- Specialized Oncology Support:
Ambulances are equipped with trained paramedics knowledgeable in oncology care, monitoring patientsŌĆÖ vital signs and administering emergency interventions as needed.
- Oxygen Support:
For patients with compromised breathing due to cancer or treatment side effects, GoAid provides oxygen cylinders and monitoring during transit.
- Continuous Monitoring:
Vital signs, pain levels, and overall condition are continuously assessed by paramedics. This ensures patient safety throughout the journey.
- Intercity Patient Transport:
GoAid offers interstate ambulance services. This enables cancer patients to reach specialized hospitals in other cities for treatment or follow-ups.
- Comfortable and Safe Travel:
Ambulances are designed for patient comfort, with reclining seats, climate control, and smooth ride to minimize physical strain.
- 24/7 Availability:
Cancer patients can access GoAid services any time, day or night. This includes weekends and holidays. This ensures support is always available.
- Emergency Medical Equipment:
Vehicles carry essential emergency medical tools. This includes IV fluids, first aid kits, and monitoring devices, for immediate response during transport.
- Coordination with Hospitals:
Paramedics communicate with hospital teams en route. This ensures the receiving facility is prepared for immediate treatment upon arrival.
- Affordable and Government-Approved Services:
GoAid provides high-quality ambulance support at reasonable rates, approved by authorities. This makes it accessible for patients across India.
Know More: Connections Between Air Quality & Pregnancy Risks
Available Treatment Options and Medical Guidance for Stomach Cancer
Proper treatment and guidance are crucial for managing stomach cancer and improving survival outcomes.
- Surgery (Gastrectomy):
Surgical removal of part or all of the stomach is the most common treatment for localized cancer. Surgeons may also remove nearby lymph nodes to prevent metastasis, restoring digestive function while aiming to remove all malignant tissue.
- Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy cancer cells or slow their growth. It can be administered before surgery (neoadjuvant) to shrink tumors or after surgery (adjuvant) to prevent recurrence and improve survival rates.
- Radiation Therapy:
Targeted radiation destroys cancer cells while preserving healthy tissue. Often combined with chemotherapy, it can reduce tumor size, relieve symptoms, and improve treatment outcomes.
- Targeted Therapy:
These drugs focus on specific molecules involved in cancer growth. This minimizes damage to normal cells. Targeted therapy is effective in advanced gastric cancer and may be combined with other treatments.
- Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy boosts the patientŌĆÖs immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. It is especially beneficial for advanced or recurrent stomach cancer. This provides longer-term disease control.
Tips for Caring for a Patient with Stomach Cancer
Caring for a stomach cancer patient requires patience, vigilance, and holistic support to improve comfort and treatment outcomes.
- Ensure Proper Nutrition:
Provide a balanced, easily digestible diet to maintain strength and support recovery during treatment.
- Monitor Symptoms Daily:
Keep track of pain, nausea, and digestion issues to promptly inform medical teams.
- Encourage Hydration:
Ensure adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration and support overall health.
- Assist with Medication Adherence:
Help patients follow prescribed treatment schedules accurately to enhance therapy effectiveness.
- Maintain Clean and Comfortable Environment:
A tidy, calm, and hygienic space reduces infection risks and promotes emotional well-being.
- Support Emotional Health:
Offer encouragement, listen actively, and provide psychological support to reduce stress and anxiety.
- Accompany for Medical Appointments:
Help with hospital visits, lab tests, and therapy sessions to ensure timely medical care.
- Limit Exposure to Infection:
Avoid crowded places and maintain proper hygiene to prevent infections, especially during chemotherapy.
- Assist in Gentle Physical Activity:
Light exercises or short walks improve circulation and help maintain muscle strength, with doctorŌĆÖs guidance.
- Educate About Early Warning Signs:
Teach family members to recognize symptoms like vomiting blood, severe pain, or sudden weakness. This ensures prompt emergency care via GoAid Cancer Ambulance Service.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have provided you all the details about What is Stomach Cancer (Gastric Cancer). Early recognition of symptoms, understanding causes and risk factors, and timely treatment are vital.
GoAid Cancer Ambulance Service ensures safe, rapid transport and emergency support. This bridges the gap between symptom onset and professional medical care, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.